1972 Pacific hurricane season
| Season summary map | |
| First storm formed | June 1, 1972 |
|---|---|
| Last storm dissipated | November 20, 1972 |
| Strongest storm | Celeste – 940 mbar (hPa) (27.77 inHg), 135 mph (215 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Total depressions | 20 |
| Total storms | 14 |
| Hurricanes | 8 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 4 |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | At least $75,000 (1972 USD) |
| Pacific hurricane seasons 1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974 |
|
The 1972 Pacific hurricane season was an ongoing event in tropical cyclone meteorology. There were few notable storms this year. No one was killed and storm effects were generally not serious. The most notable systems were Hurricane Celeste and Joanne. Celeste was the strongest storm of the season, and caused heavy damage to Johnston Atoll. Hurricane Joanne brought gale force the Continental United States and caused flooding in Arizona and northern Mexico. The only other system to directly impact land was Hurricane Annette.
The season began on May 15, 1972 in the east Pacific, and on June 1, 1972 in the central Pacific. It ended on November 30, 1972. These dates conventionally delimit the period of time when tropical cyclones form in the east Pacific Ocean. This season had a below average number of storms. There were twenty tropical cyclones, four of which were in the central Pacific. Of those, four were tropical storms, eight were hurricanes, and four were major hurricanes that reached Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. In the central Pacific, two tropical storms and two tropical depressions formed. One of the depressions and one of the storms crossed the dateline to become typhoons in the 1972 Pacific typhoon season.
Storms
Of this season's fourteen named tropical cyclones, twelve formed in the eastern Pacific and two in the central. Both central Pacific tropical cyclones were tropical storms. Of the eastern Pacific systems, four were tropical storms and eight were hurricanes. Of those eight hurricanes, four were major hurricanes because they peaked as Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale.[1] These totals are below the long-term averages of fifteen named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes.[2] At the time, it was the central Pacific's busiest season.[3]
Hurricane Annette
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | June 1 – June 7 | ||
| Intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min), 993 mbar (hPa) | ||
On June 1, a tropical disturbance organized into a tropical storm. It slowly moved north and then recurved to the northeast as it accelerated slightly. It intensified into a hurricane on June 4. It remained at that strength for one day. Annette then began weakening. As a tropical storm, Annette made landfall in southeast of Manzanillo on June 7. The next day, it dissipated inland.[4]
Annette brought several days of rainy weather to parts of Mexico. However, no deaths or damage were attributed to this tropical cyclone.[4]
Tropical Depression Two
Tropical Depression Two existed from June 27 to June 28. It paralleled the coast of Mexico without making landfall.[3]
Tropical Depression Three
Tropical Depression Three formed on July 4 and dissipated two days later. It moved westward while out to sea and never approached land.[3]
Tropical Storm Bonny
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | July 27 – July 30 | ||
| Intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min), 996 mbar (hPa) | ||
Only July 27, fifty days after the dissipation of Tropical Depression Annette, an area of clouds southwest of Manzanillo developed a closed circulation and became a tropical depression. The next day, it strengthened into a tropical storm. Heading generally west northwest, Bonny peaked in intensity on July 28. It weakened after that, and dissipated July 30. Bonny never came near land and caused no known impact.[4]
Hurricane Celeste
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 6 – August 22 | ||
| Intensity | 135 mph (215 km/h) (1-min), 940 mbar (hPa) | ||
On August 6, a tropical disturbance developed into a tropical storm, skipping the depression stage. It edged south until August 8. At that point, it turned to the west. It would continue in that general direction until it dissipated. Celeste intensified into a hurricane on August 10. It then left the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility and entered the central Pacific.[4] Celeste continued intensifying and eventually peaked as a Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale.[5] Celeste's Category 4 winds and central pressure of 940 millibars (840 hPa) made it the most intense cyclone of the season. After that, Celeste steadily weakened.[1] After turning north, it dissipated on August 22 due wind shear.[5]
Celeste harassed several ships during its existence. The most serious incident involved a sailing vessel called the Regina Marina. On August 9, that ship was flooded and had to issue a distress call. It was spotted by a hurricane hunter and was reached and towed to safety by another ship, the Vishea Trith, and later on, the USCGC Mellon. Two people aboard the Regina Marina were treated for injuries.[4] Celeste passed close to Johnston Atoll and was the first recorded hurricane to hit that island.[3] Many buildings on the weather station on the island lost roof tiles, and parts of most buildings were sandblasted by the wind. Celeste brought the highest recorded sustained winds in the station's thirteen years of operation, and the lowest barometric pressure ever recorded at Johnston at the time. A total of 6.21 inches (160 mm) of rain was recorded by a rain gauge; this may be an underestimate due to the gauge's funnel being partly blocked by a lump of coral.[5] Program 437, an anti-satellite weapons system, was destroyed by the hurricane.[6] On Johnston, no casualties were reported due to evacuations of the island's inhabitants. High waves also pounded the Puna, Kau, and South Kona Coasts of the Big Island. An exact estimate of damage is not available.[5]
At the time, Celeste was longest-lasting Pacific hurricane with a lifespan of 16.25 days; that record was tied next season by Hurricane Doreen and outrun by Hurricane Fico in 1978. It remains the ninth-longest lasting Pacific hurricane, tied with 2005's Kenneth and 1973's Doreen.[1]
Hurricane Diana
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 11 – August 20 | ||
| Intensity | 110 mph (175 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
On August 11, a tropical storm formed. It headed to the west northwest and strengthened into a hurricane on August 12. Diana then turned to the northwest, and peaked in intensity on August 1. It then headed west, and crossed into the central Pacific as a Category 1 hurricane.[4] Shortly after crossing the basin boundary on a path directly towards the Hawaiian Islands, Diana weakened into a tropical storm. On August 18, Diana turned to the northwest. It dissipated two days later.[5]
Diana threatened the Hawaiian Islands enough to warrant the issuance of a tropical storm warning. Although it never made landfall, Diana dumped very heavy rain on the Big Island, though without flooding; the highest total was 10 inches (250 mm) somewhere northeast of Hilo. At Vacationland, surf swept four homes off their foundations, doing extensive damage to one of them. Another home was flooded. Debris was carried inland, and 200 feet (60 m) of private roads were washed away.[5] The cost of damage to the extensively damaged house was $75,000 (1972 USD; $394 thousand 2012 USD), furnishings excluded.[3]
Hurricane Estelle
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 15 – August 22 | ||
| Intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
A swirl of thunderstorms near Clipperton Island became a tropical depression on August 15. It moved generally northwest. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm on August 16. Estelle continued to intensify, and became a hurricane on August 19. After peaking the next day, Estelle slowly weakened. It became a tropical storm on August 20 and dissipated two days later. Hurricane Estelle spent its entire life well away from inhabited land, and consequently caused no deaths or damage.[4]
Hurricane Fernanda
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 20 – September 1 | ||
| Intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min), 948 mbar (hPa) | ||
An area of clouds south of Manzanillo developed into a tropical storm on August 20. It slowly strengthened, moving generally westnorthwest, and became a hurricane on August 22. It continued strengthening, and was briefly a Category 3 major hurricane on 24. Fernanda weakened after that, and it was a tropical storm by the time it crossed 140°W and entered the central Pacific.[4] It remained at a steady intensity until it rapidly weakened when north of Kauai on September 1. A flash flood on Waipio Stream in the Big Island's Kohala Mountains may have been due to Fernanda. Other than that, this tropical cyclone caused no known impact.[5]
Hurricane Gwen
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 22 – August 31 | ||
| Intensity | 125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min), 941 mbar (hPa) | ||
On August 22, a tropical depression formed from a disturbance. It immediately strengthened into a storm and was named Gwen. Gwen moved generally northwest, paralleling the coast of Mexico, and intensified into a hurricane on August 24. It then spent a few days heading westnorthwest before resuming its original course. The hurricane became a major hurricane on August 27. After retaining that intensity for over a day, it rapidly weakened. Gwen became a tropical storm on August 29, weakened into a depression the next day, and dissipated just after that. Hurricane Gwen caused some concern for high surf in California, including a forecast for storm surge, but only the high surf materialized. Hurricane Gwen caused no deaths or damage.[4]
Hurricane Hyacinth
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | August 28 – September 6 | ||
| Intensity | 125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min), 962 mbar (hPa) | ||
A circulation south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec organized into a tropical depression on August 28. It moved west for a day and then turned to the west northwest. It intensified into a tropical storm on August 29 and a hurricane the next day. Hyacinth peaked as a Category 3 major hurricane on August 31 through September 1. It then weakened. It also began to recurve to the north and then the northeast. Hyacinth reached its westernmost point on September 4 while a tropical storm. On September 6, it weakened into a tropical depression. It then made landfall north of San Diego, California as a remnant low later that day, but it was nearly dissipated.[4]
Hyacinth caused increased surf along the coast of California,[7] but was otherwise without serious effects.[4] Tropical Depression Hyacinth's landfall was the first in California since 1939.[1][8]
Tropical Storm Iva
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | September 14 – September 22 | ||
| Intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min), 999 mbar (hPa) | ||
South of Salina Cruz, a tropical depression formed on September 14. It paralleled the coast of Mexico until it strengthened into a tropical storm on September 16. Iva spent three days barely moving. On August 19, Iva got caught in the trade winds, headed westwards out to sea, and promptly weakened into a depression. By August 22 it was just a mass of clouds. Iva did not come near land and had no appreciable impact.[4]
Tropical Storm June
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | September 24 – September 28 | ||
| Intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
A northwestward-moving disturbance in the intertropical convergence zone developed into a tropical depression on September 24 and a storm two days later. It never strengthened much, and rapidly weakened on September 28. Tropical Storm June passed southwest of Johnston Island on September 27, but was too feeble to cause damage, only bringing gusty breezes and some rain.[5]
Tropical Depression of September 28 to October 3
A tropical depression formed September 28 east of the Hawaiian Islands. It headed towards the archipelago and dissipated on the afternoon of October 3. Later that day, its remnants dumped up to 10.5 in (270 mm) of rain on the mountains of the Big Island.[5]
Hurricane Joanne
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | September 30 – October 6 | ||
| Intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min), 971 mbar (hPa) | ||
A westward-moving area of squalls south of Mexico organized into a tropical depression on September 30. It then strengthened into a tropical storm and was named Joanne. Joanne moved west northwest, and intensified into a hurricane on October 1. It then peaked as a Category 2 hurricane on October 2. Joanne then slowed down and began to recurve, first to the north, and then the north northeast. While accelerating in that direction, Joanne made landfall near Laguna Chapala on the Baja California Peninsula as a tropical storm.[4] Joanne managed to retain a closed circulation and bring tropical storm force winds to Arizona, the first recorded time that had happened.[9] The tropical storm dissipated inland over Sonora on October 7.[4] Joanne is one of only four known Pacific hurricanes to bring gale-force winds to the Continental United States, and was the first since the 1939 California tropical storm.[10]
Heavy rainfall was reported throughout Arizona. Over 5 inches (100 mm) was measured at the Mogollon Rim. There was severe flooding in the areas of Clifton, Duncan, and Safford. Heavy rains were recorded elsewhere in the region.[9] The highest total in Mexico was 9.45 in (240 mm) in San Felipe/Mexicali.[11] Joanne caused heavy surf in California.[12] No deaths were attributed to this tropical cyclone. An exact cost of damage is unknown.[4]
Tropical Depression Thirteen
Tropical Depression Thirteen formed on October 12. It first headed southwest, then west, and performed a cyclonic loop. It headed north before sharply recurving. It dissipated on October 18.[3]
Tropical Depression of October 18 (Olga)
| Tropical depression (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | October 18 – October 18 | ||
| Intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
Just east of the dateline, the northern hemisphere component of a "cyclone twin" formed into a tropical depression October 16.[5] After crossing the dateline, it intensfied into Tropical Storm Olga of the 1972 Pacific typhoon season. After passing through the Marshalls as a tropical storm, Olga intensified into a typhoon on October 25. It then swung through part of the Northern Marianas Islands before it was absorbed by a front near Honshū on October 29. As the NMI had already been hit by Typhoon Marie three weeks earlier, little damage was reported.[13]
Tropical Storm Kathleen
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | October 18 – October 19 | ||
| Intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
On October 18, a vortex in the intertropical convergence zone was determined to be a tropical storm through the use of satellite pictures.[4] Kathleen was a tropical storm for only eighteen hours[1] before weakening into a tropical depression and recurving to the northeast. The tropical cyclone dissipated on October 19 while out to sea west of Puerto Vallarta. No deaths or damages were reported.[4]
Tropical Storm Ruby
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | November 11 – November 14 | ||
| Intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
An area of enhanced convection in the ITCZ close to the equator formed into a tropical depression on November 11. It headed north northwest, and intensified into Tropical Storm Ruby on November 13. Ruby then abruptly turned west and crossed the dateline.[5] After becoming a typhoon just after crossing the dateline, the first time that had happened since 1967, Ruby steadily strengthened and eventually peaked as a moderately intense typhoon on November 16 while east of Taongi Atoll. It then steadily weakened as it headed west northwest, and wind shear destroyed the cyclone on November 20 when it was east of the Northern Marianas Islands. Ruby caused no deaths or damage. Of note is the fact that on November 17, Ruby had a central pressure of 983 mb (983 hPa), which is high for a 100-knot typhoon.[14]
Tropical Storm Liza
| Tropical storm (SSHS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Duration | November 13 – November 15 | ||
| Intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min), Unknown | ||
A tropical depression formed south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec on November 13. It headed nearly due east and intensified into Tropical Storm Liza on November 14. Liza degenerated into a tropical wave the next day. No deaths or damages were reported.[4] Liza was a tropical storm for less than a day.[1]
Tropical Depression Sixteen
Tropical Depression Sixteen formed on November 20. It briefly headed north and then turned to the west. It dissipated on November 21.[3]
Timeline
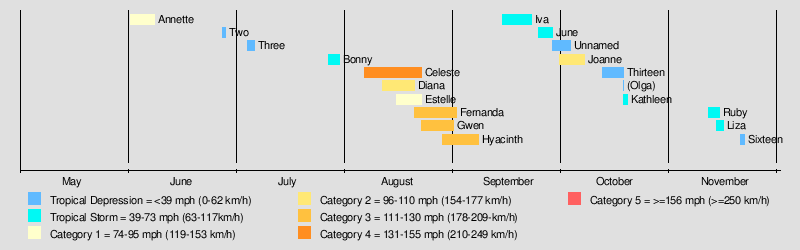
The season began from the formation of the pre-Annette tropical depression on June 1, and ended with Tropical Storm Liza losing its circulation on November 15. This is a span of 167 days. In the eastern north Pacific, one storm formed in May, one each in June and July, six in August, two in September, and one in November. In the central north Pacific, one storm formed in each of September and November. This season is tied with the 1977 and 1996 seasons for fewest tropical storms to form in July.[1] It also shares the record for busiest November in the central Pacific with 1982 season.[1]
1972 Storm Names
These names were used for storms that formed in the east Pacific ocean this season. It is the same list used in the 1968 season. No names were retired, so this list was used again in the 1976 season.
|
|
|
The central Pacific used names and numbers from the west Pacific's typhoon list. Two names — June and Ruby — were required. Of the eleven hurricane seasons from 1970-81 where central Pacific cyclones were named using the west Pacific list, this is the first and only one to use multiple names.[1]
See also
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- List of Pacific hurricane seasons
- 1972 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1972 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons: 1971–72, 1972–73
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Eastern North Pacific Tracks File 1949-2008" (plaintext). National Hurricane Center. 2009-95-29. Archived from the original on 2009-06-06. http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/tracks1949to2008_epa.txt. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ^ "Background Information: East Pacific Hurricane Season". Climate Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 2009-06-06. http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/Epac_hurr/background_information.html. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Annex A Summary of Tropical Cyclones in the Eastern North Pacific" (PDF). Annual Typhoon Report 1972. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1972atcr/pdf/annexa.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Robert A. Baum (April 1973). "Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Season of 1972" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review (American Meteorological Society) 101 (4): 339–49. Bibcode 1973MWRv..101..339B. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1973)101<0339:ENPHSO>2.3.CO;2. http://docs.lib.noaa.gov/rescue/mwr/101/mwr-101-04-0339.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "The Central Pacific Tropical Cyclone Season of 1972". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on 2009-08-14. http://www.prh.noaa.gov/cphc/summaries/1972.php. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- ^ Clayton K.S. Chun (PDF). Shooting Down a Star. pp. 30–31. ISBN 158566071X. Archived from the original on 2006-05-16. http://web.archive.org/web/20060516010051/http://aupress.au.af.mil/CADRE_Papers/PDF_Bin/chun.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- ^ "Beaches Crowded as Holiday Begins" (PDF). Oxnard Press-Courier. 1972-09-03. p. 1. Archived from the original on 2009-08-14. http://www.thehurricanearchive.com/Viewer.aspx?img=81883690_clean&firstvisit=true&src=search¤tResult=0¤tPage=0. Retrieved 2009-08-11.
- ^ Jack Williams (2005-05-17). "Background: California's tropical storms". USA Today. http://www.usatoday.com/weather/whhcalif.htm. Retrieved 2009-08-11.
- ^ a b "...Top Arizona Hurricane/Tropical Storm Events...". Archived from the original on 2009-06-17. http://www.wrh.noaa.gov/psr/tropics/hurricanes.htm. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ^ Michael Chenoweth & Christopher Landsea. "The San Diego Hurricane of 2 October 1858" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 85 (11): 1689–1697. Archived from the original on 2009-06-17. http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/Landsea/chenowethlandsea.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ^ David M. Roth. "Hurricane Joanne - October 5–8, 1972" (GIF). Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 2009-08-16. http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/tropical/rain/joanne1972filledrainblk.gif. Retrieved 2009-08-14.
- ^ "Calif. Desert Normal after Flash Floods" (PDF). Long Beach Press-Telegram. 1972-10-05. p. 17. Archived from the original on 2009-08-16. http://www.thehurricanearchive.com/Viewer.aspx?img=46451698_clean&firstvisit=true&src=search¤tResult=9¤tPage=0. Retrieved 2009-08-14.
- ^ "Olga" (PDF). Annual Typhoon Report 1972. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1972atcr/pdf/wnp/28.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-14.
- ^ "Ruby" (PDF). Annual Typhoon Report 1972. Joint Typhoon Warning Center. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1972atcr/pdf/wnp/30.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-14.
External links
- Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Season of 1972
- CPHC Season Summary
- ATCR Eastern Pacific summary
- Unisys Storm Tracks
- Arizona's tropical cyclones
|
Tropical cyclones of the 1972 Pacific hurricane season |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Book · Category · Portal · WikiProject · Commons |
|
|
|||||